Evolution of AI: Understanding Machine Learning vs Deep Learning

Imagine a scene where computers respond to your requests and evolve through experience to solve problems once confined to science fiction. This is the promise of Machine Learning and Deep Learning—two transformative technologies. While people often use these terms interchangeably, they are distinct, each contributing uniquely to Artificial Intelligence (AI). According to Andrew Ng, "AI is the new electricity," underscoring how these technologies will shape future industries and lifestyles. To understand the true potential of AI in a data-driven world, it is essential to grasp these two cornerstones.
Artificial Intelligence and Its Subsets
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a collection of technologies that enable computers to perform sophisticated tasks, such as data analysis, decision-making, speech and text comprehension, and vision [1]. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are both subsets of AI, with ML focusing on improving decision-making abilities and DL imitating the human brain's processes.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that develops algorithms enabling systems to learn from data autonomously [2] [4]. ML algorithms use large datasets to identify patterns, make predictions, or generate decisions. ML is categorized into two main types: Supervised Learning and Unsupervised Learning.
Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning uses labeled data to learn the relationship between input and output. For example, the dataset contains input features (attributes) and corresponding output labels (target values). The algorithm learns from this labeled data to make accurate predictions [6].
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning, on the other hand, involves detecting patterns in unlabeled data. This type of ML automatically groups data based on intrinsic properties (clustering) or extracts key features to make meaningful insights [5].
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning (DL) is a specialized subset of ML that uses multilayered neural networks to process and analyze information. It is inspired by the human brain's neural network, with algorithms designed to excel in tasks like computer vision, speech recognition, and natural language processing [8].
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) mimic the human brain using artificial neurons arranged in layers. Data enters through the input layer, is processed through several hidden layers, and finally reaches the output layer, which produces the desired result. There are various types of neural networks, including Feedforward Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Long Short-Term Memory Networks [7] [11].
Applications of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine Learning and Deep Learning are driving innovation across various industries. Here are some common applications:
- Machine Learning: Image recognition, speech recognition, recommendation systems, fraud detection, self-driving cars, medical diagnosis, stock market trading [12].
- Deep Learning: Computer vision, natural language processing, reinforcement learning, generative AI [8].
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their potential, both Machine Learning and Deep Learning face several challenges, such as lack of data, high computational costs, and a lack of transparency in decision-making. Nevertheless, these technologies continue to evolve, and when properly harnessed, they can usher in an AI-driven world that offers new business perspectives and improved performance in various fields.
Understanding the differences between Machine Learning and Deep Learning is crucial in realizing the broader applications and limitations of AI technologies, which continue to shape industries and our way of life.
Bibliography
- 1) “What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?” | Google Cloud
- 2) “Deep learning vs machine learning” | Google Cloud
- 3) “Difference Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning” | GeeksforGeeks
- 4) What Is Machine Learning (ML)? | IBM
- 5) “Supervised and Unsupervised Learning” | GeeksforGeeks
- 6) “Supervised Machine Learning” | GeeksforGeeks
- 7) “What is a neural network?” | GeeksforGeeks
- 8) “What Is Deep Learning?” | IBM
- 9) “Introduction to Deep Learning” | GeeksforGeeks
- 10) “Artificial Neural Networks and its Applications” | GeeksforGeeks
- 12) “Applications of Machine Learning” | GeeksforGeeks
Similar Post You May Like
-
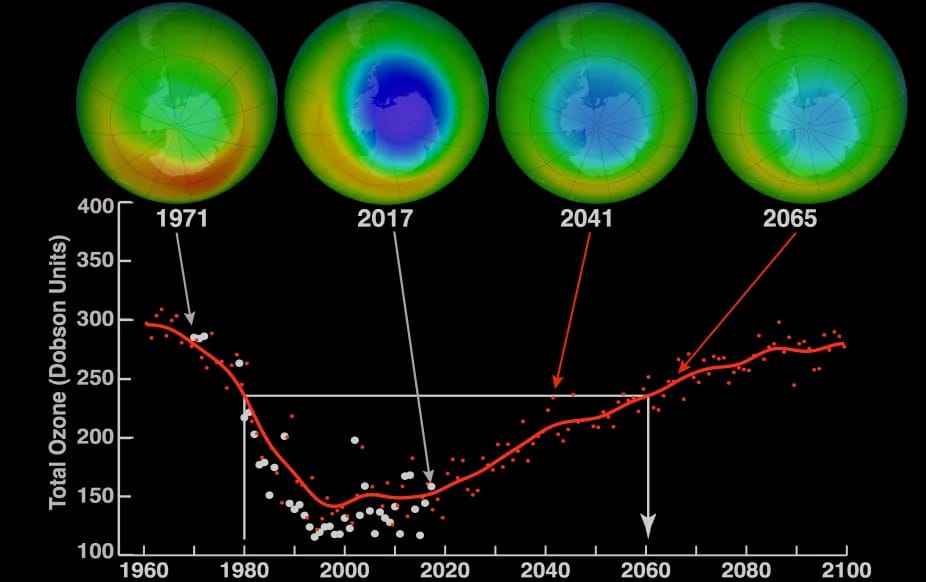
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.