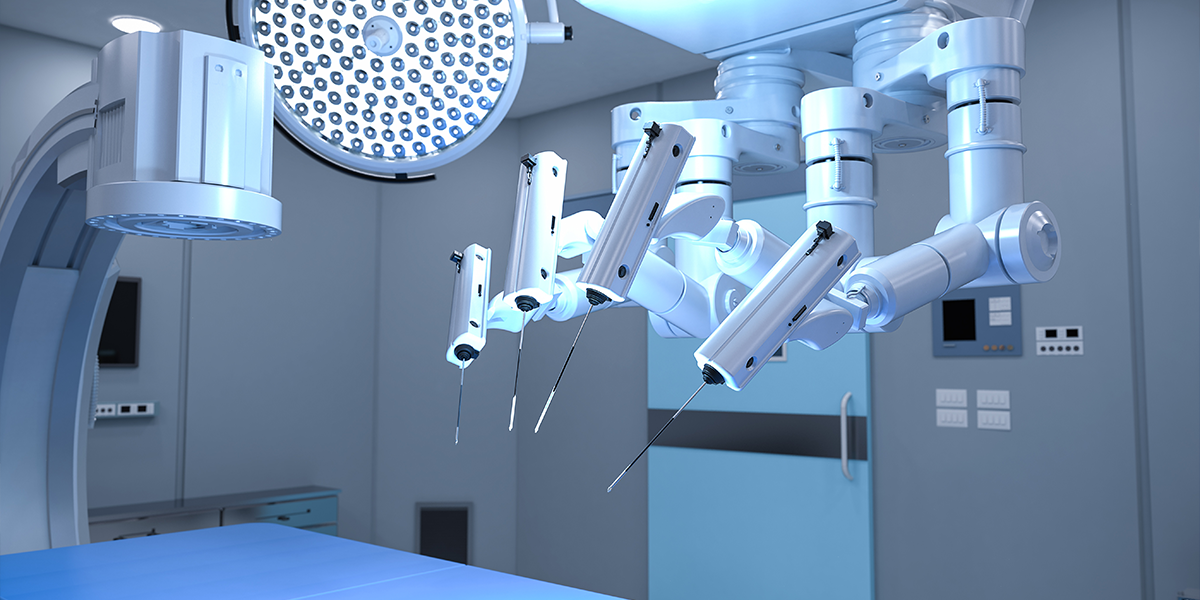
Healing Hands of Steel - Robot-Assisted Surgery
"I fear that AI may replace humans altogether." – Stephen Hawking
When Stephen Hawking made this statement, he was onto something because it's definitely replacing our surgeons. With the heavy emergence of artificial intelligence in recent times, robot-assisted surgery has evolved astronomically, converging medicine and technology.
About half a century ago, robots made their way into operation theatres, mainly for procedures such as biopsies and hip replacements. As technology advanced, these occurrences became more frequent such as in simple laparoscopic surgery, where a robotic arm named AESOP HR, introduced in the 1990s, provided the surgeon with a view inside the human body, proving to be a “third hand” with voice control on many aspects of the surgery, such as the position of the operating room table.
In 1995, the da Vinci Robotic Surgery System was presented, which was an even more advanced way to perform laparoscopies (yes, Leonardo da Vinci has accomplishments other than the Mona Lisa). This machine was able to replicate the surgeon's movements, as they guided it through a joystick and a monitor. Now instead of four people standing around a patient, four robotic arms pry in a patient, all controlled by a trained surgeon. This system has been used for over 10 million procedures to date, with a success rate of up to 95%.
These robots have been designed and evolved in order to perform minimally invasive surgeries, meaning procedures that require smaller incisions, less blood loss and scarring, lesser chance of infection and faster recovery. Such equipment also caters to the needs of surgeons, providing stability and reduction of human error since machinery is not subject to human flaws (no more coffee runs). High-definition cameras and master control consoles make intricate procedures be carried out more precisely. As a result, postoperative pains are minimized, surgeries take place faster and the recovery time is condensed. Robot-assisted surgery has, hence, been proven to be favored and recommended by medical professionals.
In spite of the colossal advantages, it is still opposed by many. From a third-person perspective, this must look straightforward but those given this option have their uncertainties. While it has a very high success rate, robotic surgery cannot be performed in specific circumstances, such as scar tissue from a previous incision, as a result of which the surgeon will resort to the usual open surgery. Moreover, in a rare occurrence, a technological malfunction may take place since machinery is after all manmade. This malfunction might cause nerve and tissue damage or in more serious malfunctions, death. The surgeon manipulating the machine must also be thoroughly equipped and know the process inside out since a simple mistake in inputting data might lead to serious consequences. In the bargain, such equipment is extremely costly and might not be an accessible option.
Scientists are continuing to make headway in refining artificial intelligence to obtain improved results. It is believed that the da Vinci Surgery System has reached the end of its popularity and more compressed, smaller robots are being introduced such as SurgiBot and MiroSure. These would be portable and more accessible and aim to reduce the invasiveness of the surgical process as a whole.
Technology has come a long way in the medical field and with the emergence of new and improved robots, the success rates of surgical procedures will proceed to increase. With these advancements, medical experts and policy-makers must keep up to date and evolve with artificial intelligence to ensure just use of this blessing. With each advancement, robot-assisted surgery inches closer to perfection, promising a new era of precision, healing and hope.
Similar Post You May Like
-
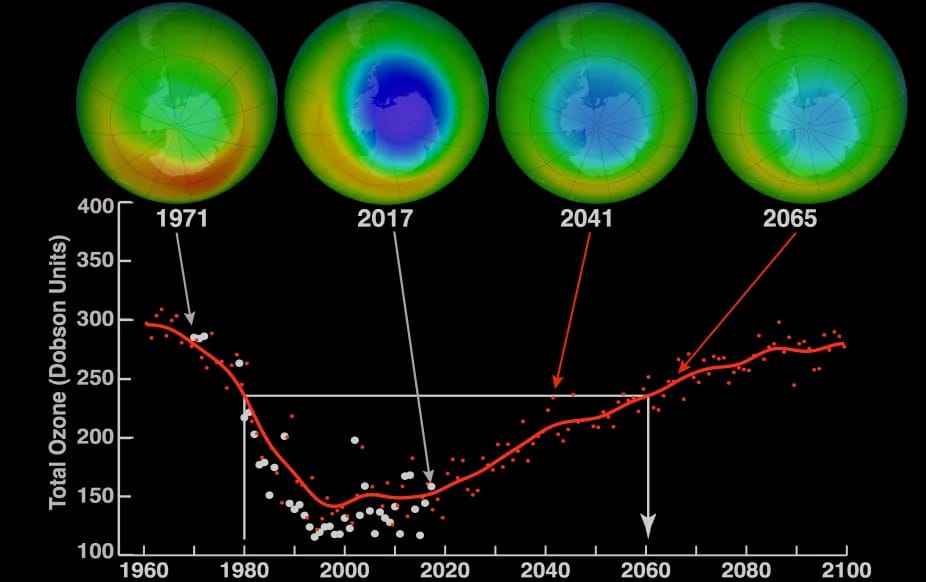
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.