A Crossroads for Humanity: Environmental Ethics and the Fight for a Sustainable Future

Imagine a world devoid of the vibrant symphony of birdsong, replaced by the monotonous hum of urban sprawl. This bleak scenario underscores the urgent need for environmental ethics, a philosophical movement gaining traction as humanity grapples with the consequences of its actions on the planet.
Environmental ethics delves into the moral relationship between humans and the environment. It asks critical questions: What are our obligations to the natural world? How can we ensure its well-being alongside our own? As the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy aptly states, it's "the discipline in philosophy that studies the moral relationship of human beings to, and also the value and moral status of, the environment and its non-human contents."
The urgency of climate change has brought environmental ethics to the forefront. Rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and scorching temperatures paint a stark picture of our environmental impact. While this concern is paramount today, the seeds of environmental ethics were sown much earlier. The 1960s witnessed a growing awareness of the unintended consequences of the industrial revolution and technological advancements. Pioneering works like Rachel Carson's "Silent Spring" and Paul Ehrlich's "Population Bomb" served as stark reminders of the detrimental effects of unchecked human activity. These works highlighted the critical need for a paradigm shift in our relationship with the environment.
Environmental ethics encompasses diverse approaches, categorized into three main schools of thought:
-
Libertarian Extension:
This view emphasizes individual rights, advocating for a biocentric model where both humans and non-human entities have intrinsic value. It promotes respect and consideration between all living things, suggesting a fundamental right to exist and flourish.
-
Ecological Extension:
This philosophy prioritizes preserving and nurturing the natural world. It highlights human responsibility for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the health of the entire system. Proponents of this approach emphasize the interconnectedness of all living things and the crucial role humans play in ensuring sustainability for future generations.
-
Conservation Ethics:
This philosophy focuses on responsible and judicious use of natural resources. It advocates for a balanced approach where humans can utilize natural resources to meet their needs while prioritizing their long-term conservation. This approach ensures that future generations inherit a healthy and resource-rich planet.
Renewable energy sources exemplify environmental ethics in action. Solar, wind, and hydropower are all naturally replenished resources. By harnessing these clean alternatives, we can move away from polluting fossil fuels and embrace more sustainable practices.
In essence, libertarian extension emphasizes human rights alongside those of nature, ecological ethics encourage cooperation with nature for mutual benefit, and conservation ethics advocate for responsible resource protection. Each approach offers valuable insights, fostering ongoing discussions about the best way forward in navigating our complex relationship with the environment.
Core Principles of Environmental Ethics:
- Respect for Nature:
Nature isn't merely a resource to be exploited; it deserves protection and preservation for its intrinsic value.
- Interdependence:
Humans are intricately linked to other species and ecosystems. Maintaining ecological balance is crucial for our own survival as well as the well-being of countless other creatures.
- Sustainability:
Responsible resource use and ecosystem preservation are essential for long-term human well-being and the well-being of all living things.
- Human Responsibility:
We are accountable for the environmental consequences of our actions, both positive and negative. We have a moral obligation to act in a way that protects the planet for future generations.
- Equity:
Striving for a world where rights and well-being are protected for all living beings, human and non-human alike.
Environmental ethics has undergone a significant transformation. It has evolved from a niche concept to a critical field of study informing policy, influencing decisions, and offering a framework for ethical decision-making. As we stand at a crossroads, environmental ethics provides a roadmap towards a more sustainable future. By embracing these principles and fostering international cooperation, we can work together to build a world where nature thrives alongside humanity.
Similar Post You May Like
-
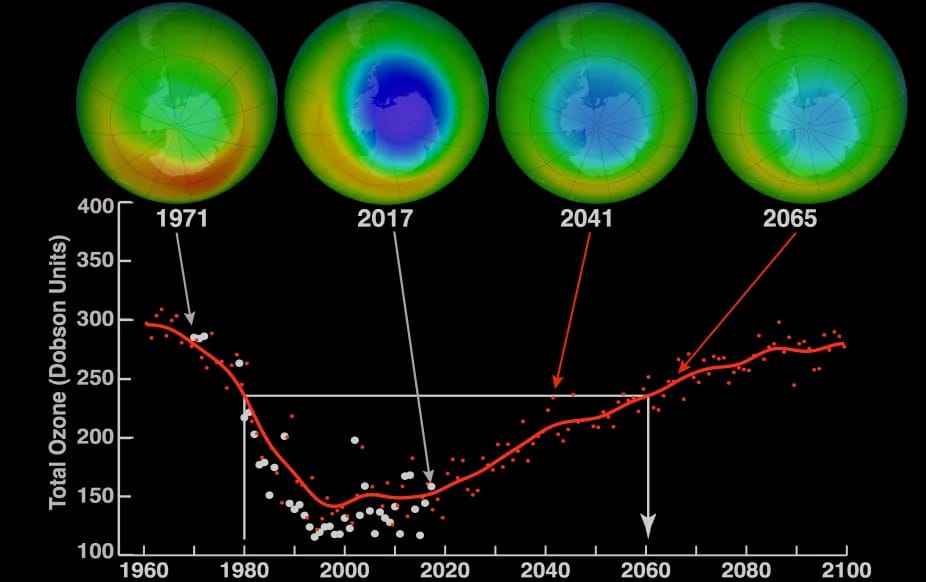
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.