Alchemy: the Myth and Its Scientific Legacy

Alchemy, often shrouded in mystery and mysticism, has a complex history that spans centuries and encompasses both mystical beliefs and proto-scientific practices. While traditionally associated with attempts to transmute base metals into gold and discover the elixir of life, alchemy also made significant contributions to the development of modern chemistry and scientific inquiry. In this article, we delve into the history of alchemy, its cultural and philosophical significance, and its lasting legacy in the evolution of scientific thought.
The Origins of Alchemy: From Ancient Traditions to Medieval Europe
The roots of alchemy can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China, where early practitioners sought to unlock the secrets of nature, metals, and the cosmos. Alchemy in its early stages encompassed a blend of philosophical speculation, spiritual beliefs, and practical experimentation aimed at understanding the nature of matter, transformation processes, and the quest for spiritual enlightenment.
During the medieval period in Europe, alchemy flourished as a secretive and esoteric art practiced by alchemists who pursued the goals of transmutation, purification, and the discovery of the philosopher's stone—a legendary substance believed to possess the power to transform base metals into gold and grant immortality.
Alchemy's Contributions to Early Chemistry: Experimental Inquiry and Chemical Processes
Despite its mystical connotations, alchemy laid the groundwork for early chemical experimentation, laboratory practices, and the systematic study of matter. Alchemists developed techniques for distillation, sublimation, precipitation, and purification of substances, laying the foundation for modern chemical processes and laboratory equipment.
Alchemy's focus on observation, experimentation, and empirical methods contributed to advancements in metallurgy, pharmacology, and the study of chemical reactions. Alchemists' quest for transmutation led to discoveries and refinements in techniques such as alloying metals, extracting medicinal compounds from plants, and developing methods for glassmaking and ceramics production.
Alchemy's Influence on Philosophical and Spiritual Thought: Hermeticism and Esoteric Traditions
Beyond its practical applications, alchemy had a profound influence on philosophical and spiritual thought, particularly through its association with Hermeticism—an ancient tradition that emphasized the unity of the cosmos, the interconnectedness of the microcosm and macrocosm, and the pursuit of inner transformation.
Hermetic texts, such as the "Emerald Tablet" attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, conveyed symbolic teachings about the union of opposites, the transmutation of the soul, and the quest for spiritual enlightenment. Alchemical symbolism, allegories, and metaphors became vehicles for conveying deeper philosophical concepts, inner alchemy practices, and the search for universal truths.
Alchemy's Transition to Modern Chemistry: The Chemical Revolution and Scientific Method
The transition from alchemy to modern chemistry occurred during the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, marked by the emergence of systematic scientific inquiry, empirical methods, and the development of the scientific method. Alchemists' investigations into the properties of substances, chemical reactions, and the nature of matter laid the groundwork for the scientific principles of atomic theory, stoichiometry, and chemical elements.
Key figures in the transition from alchemy to modern chemistry include Robert Boyle, Antoine Lavoisier, and Johann Becher, who pioneered experimental methods, quantitative analysis, and the recognition of chemical elements and compounds. The establishment of scientific societies, journals, and academic institutions further solidified chemistry as a distinct scientific discipline based on empirical evidence, reproducible experiments, and theoretical frameworks.
Alchemy's Legacy in Modern Science: Symbolism, Cultural Influence, and Historical Perspectives
While alchemy as a mystical and speculative practice faded with the rise of modern science, its legacy endures in symbolic imagery, cultural references, and historical perspectives on the evolution of scientific thought. Alchemical symbolism, such as the philosopher's stone, the alchemical stages of transformation (nigredo, albedo, citrinitas, rubedo), and the alchemical marriage of opposites, continues to inspire artistic, literary, and philosophical interpretations.
Moreover, alchemy's emphasis on transformation, synthesis, and the search for hidden truths resonates with themes in psychology, mythology, and spiritual traditions, contributing to its enduring appeal and relevance in contemporary discourse.
Conclusion: Unveiling Alchemy's Dual Nature as Myth and Science
In conclusion, alchemy's legacy embodies a dual nature—a blend of mythological symbolism, spiritual aspirations, and proto-scientific practices that laid the groundwork for modern chemistry and scientific inquiry. While alchemy's mystical pursuits of transmutation and spiritual enlightenment may seem fantastical, its contributions to experimental methods, laboratory techniques, and the systematic study of matter were instrumental in shaping the trajectory of scientific thought.
By exploring the history of alchemy, its cultural significance, and its enduring influence on scientific, philosophical, and artistic endeavors, we gain insights into the complex interplay between myth and science, imagination and experimentation, and the quest for knowledge that transcends temporal boundaries and cultural contexts. Alchemy's journey from ancient traditions to modern science serves as a testament to the enduring human quest for understanding, transformation, and the pursuit of truth in the ever-evolving tapestry of human knowledge and discovery.
Similar Post You May Like
-
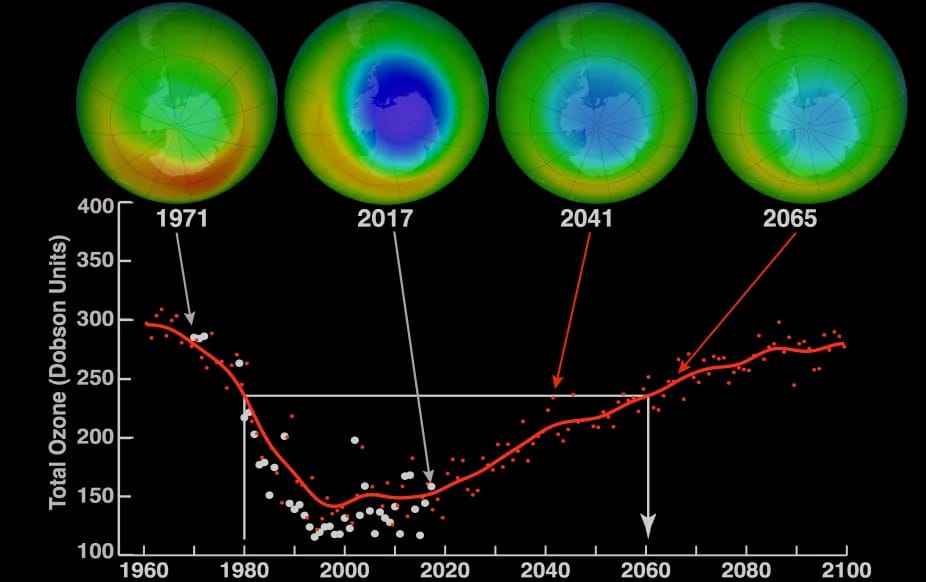
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.